
Internet giant Google has recently been sharpening its focus on dominating AI.
Not content with its almost monopolistic hold of internet searches, Google has a 90% market share.
The company sees AI as a way of further increasing its relevance and dominance.
Already many of Google’s most popular applications, such as its voice assistant and search engine are driven by Google AI developed tools.
It’s not just Google benefitting from the company’s developments in AI.
Google AI and machine learning help 20th Century Fox develop scripts and predict box office revenue and growth.
Prompted by the quick growth of AI, Google has created its Google AI division.
From driving Google Assistant to transforming healthcare and helping scientists make world-changing discoveries AI is already impacting.
Google’s AI applications are not only transforming cancer diagnosis methods but are also allowing physicians to create personalized treatment programs.
However, Google is also aiming to make Artificial Intelligence available to anyone.
This dovetails with one of the company’s stated aims; to organize the world’s information, making it accessible and usable for everyone.
Google’s versatile TensorFlow framework is an open-source platform.
TensorFlow houses a number of AI-related systems.
This means that developers can use it as a one-stop-shop for application development.
Not only does this make AI development easier and more accessible, but it helps to increase Google’s influence in the field.
Table of Contents
Google AI is Aiming for World Domination
In the course of this article, we’ll explore the formation of Google AI, highlighting the main reasons for its creation.
Excitingly, we’ll also look at some of the many different ways in which Google AI is already impacting on the wider world.
As well as the benefits for the parent company we will see that Google AIs developments are benefitting other companies and organizations.
Google AI aims to drive innovation by collaborating with others.
From developments in health care and conservation and to image generation and responsive voice assistants.
We will also learn about’s Google AI venture capitalist investment including it’s dedicated AI fund Gradient Ventures investing in a range of cutting edge technology companies.
Read on to learn how Google AI is already transforming how we see and interact with the world.
The Formation of Google AI
Google AI is a division of Google, hosting the company’s AI-related work and tools.
As the name suggests its purpose is to explore and develop artificial intelligence-based applications.
The formation of this division was announced in 2017 at the Google I/O by CEO Sundar Pichai.
Pichai also set out how the division would focus its attention on three specific roles: research, tools and applied AI.
One of Pichai’s stated aims is to see the company endeavoring to open up machine learning to “hundreds of thousands of developers”.

Who is Google?
Google AI’s parent company, Google LLC, is an American multinational technology company.
Alongside Facebook, Amazon, and Apple they make up the Big Four technology companies. Google AI helps to power and evolve a wide range of services and features, including their ubiquitous search engine, software, hardware, and cloud computing.
Google was formed in 1998 by Stanford University Ph.D. students Sergey Brin and Larry Page.
Today the company is today based in Mountain View, California.
Since inception, Google has been at the heart of technological progress.
The company has developed a number of commonly used applications and services.
These include Gmail, Google Earth, YouTube, and the Google Home smart speaker.
Google’s constant drive to progress and develop has seen them acquire and partner with other innovation driving startups and operations.
Recently Google’s ubiquity has led to a number of privacy concerns.
There have also been claims of censorship, search neutrality, and tax avoidance.
However, this hasn’t stopped Google from growing in size, or usage.
Today the company is looking to AI to further enhance and optimize its services and the wider world.
For this reason, Google AI sits at the heart of the future of Google.

Google AI is Transforming Healthcare and Biosciences
Machine learning and AI have a myriad of potential applications.
One area where they could make a real impact is in the fields of healthcare and biosciences.
From research and drug development to accessing test results and improving patient care AI has a big role to play.
Medical Applications of Deep Learning
Deep learning has transformed computer vision, turning it into a practical, easily accessible technology.
Researchers at Google AI noted how this technology was already capable of identifying basic things such as dog breeds.
Curious they began to explore the possibility of a more useful application.
They set to work developing systems capable of analyzing medical images for signs of disease.
This research has been done alongside medical practitioners, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the system.
One field where Google AI’s research is already making an impact is in sight loss.

Google AI’s Work on Detecting Eye Disease
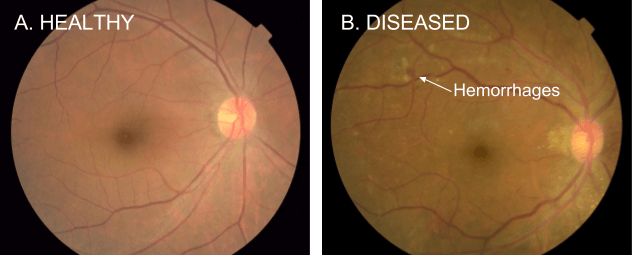
Worldwide, nearly 415 million diabetics risk losing their sight to a condition called Diabetic Retinopathy.
While this disease can cause blindness, if it is caught early enough it is treatable.
However many patients, in different parts of the world, do not have access to specialists able to detect the disease.
Developers at Google AI are working on machine learning systems capable of identifying the disease.
This application is designed to be easy to use in remote, and underserved areas of the world.
Once rolled out, the system will speed up diagnosis times, potentially saving the sight of many people.
Their work was outlined in the paper, “Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy in Retinal Fundus Photographs.”
The paper outlined how deep learning algorithms are able to recognize signs of Diabetic Retinopathy in retinal photographs.
Without this application a specialist must examine photographs of the eye, looking for signs of disease.
This manual process is also used to determine the severity of the condition, by assessing what legions are present.
While this process is reliable it is also incredibly time-consuming.
It also requires specialist training.
In underserved areas, people are at risk of losing all, or parts of their sight before a diagnosis is made.
MORE – Google’s DeepMind Beats Doctors at Detecting 50 Eye Diseases Just by Looking at Scans
MORE – Google AI Can Predict Potential Heart Disease By Looking at the Eyes
These Models Will Continue to Be Refined
Working alongside doctors in the US and India, Google AI developers combined a dataset comprising of 128,000 images.
These images were then evaluated by ophthalmologists.
Once validated the system was trained on the dataset.
This created a deep neural network capable of detecting diabetic retinopathy.
The trained algorithm was tested on two different clinical validation sets, each comprising of around 12,000 images.
These results were compared with the decisions made by trained ophthalmologists.
The comparisons revealed that the algorithm performed on par with the trained professionals.
While these results are exciting, developers are not yet content.
Google AI plans to carry on working with retinal specialists, defining more robust reference standards.
These will be used to further improve the performance of the algorithm.
Learning to Read 3D Images
Interpreting 2D fundus photographs is only part of the process of identifying eye disease.
In more complex cases Optical Coherence Tomography, 3D imaging technology, creates a detailed representation of the retina’s layers.
Google AI’s colleagues at DeepMind, the UK based startup, are already applying machine learning to OCT and 3D imaging.
It is hoped that the two applications will be able to work alongside each other.
This will help to quickly diagnose a range of eye diseases.
Lead researcher Rory Sayres, Ph.D., has described how exciting this application of AI is, “AI and physicians working together can be more accurate than either alone.”
This application and similar solutions will help to improve patient care.
They will also allow trained physicians to better focus their time and expertise.
MORE – Top 10 Ways Artificial Intelligence is Impacting Healthcare
MORE – Artificial Intelligence in Medicine – Top 10 Applications
Deep Learning to aid Cancer Detection
A similar application in the field of medical diagnosis is the use of deep learning and AI to detect cancer.
Researchers at Google AI have so far focused on developing algorithms that assist pathologists in detecting cancer in lymph node biopsies.
When performed manually, this task is complicated and time-consuming.
It also takes many years to train a human operative to competently perform this task.
Even then diagnoses can vary between pathologists.
This variation in diagnosis can lead to misdiagnosis.
This discrepancy, found in diagnosing forms of breast cancer when an agreement between pathologists may be as low as 48%.
Similarly, prostate cancer patients can also suffer from low detection and misdiagnosis rates.
This is because of the large amount of information a pathologist has to sift through.
Much of this information can be detected in different ways by different people.
Google AI’s detection algorithms are designed to complement the work of the pathologist, helping to highlight possible causes of cancer.
Applying these systems will also help to lower misdiagnosis rates.
A Focus on Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Google Ai’s algorithms were trained on images from Radboud University Medical Centre.
Initially, the system focused on breast cancer research has spread to lymph nodes adjacent to the breast.
The initial results, following training, were promising.
The team at Google AI discovered that approaches such as GoogleNet worked well however further customization was necessary.

This included training the neural networks to examine images at various different magnifications.
Eventually, once fully trained, the system was able to consistently match, or outperform, the pathologist.
The algorithm eventually reached a localization score, FROC, of 89%.
In comparison, the pathologist examining the same images and operating under no time constraints recorded a score of just 73%.
The Google AI team was further encouraged by the knowledge that their model generalized well.
It was capable of accurately reading images from different hospitals and different scanners.
The team published these exciting results in their paper “Detecting Cancer Metastases on Gigapixel Pathology Images”.
There is Still Room for Further Development
While these results and the developed algorithm are promising they are designed to be used alongside pathologists analysis.
This is because while the algorithms perform well for tasks they are trained to do.
However, they don’t yet have the knowledge, or experience, of trained human pathologists.
This means that the algorithms are unable to detect other abnormalities, such as other types of cancer or autoimmune disease.
As AI and machine learning is further developed the algorithms will become more complex and capable.
However, for now, they are designed to be a complementary tool.
The next step is to seek clinical validation and regulatory approval.
This will see the algorithms and systems being used alongside pathologists to accelerate and improve the diagnostic process.
Google AI and Applied Science
At Google AI they are combining physics and biology with computer science.
The team believes that these two distinct worlds are complimentary.
A development in one world can power advances in the other.
This belief is encouraging Google Ai’s Applied Science department to look for significant scientific breakthroughs that could benefit the wider world.
Much of this work focuses on entwining the two worlds, ensuring that this symbiotic relationship continues.
Applied Science’s Four Fields of Focus
Google AI’s Applied Science team are focusing their efforts on four fields in particular.
The first of these is Quantum Computing.
Quantum computers perform calculations based on the probability of the state of an object.
Classical computers perform calculations with measurements and binary information.
Quantum computers don’t need this information to make their calculations.
This means that they can, potentially, process far more data than classical computers.
Google’s AI quantum computing team has focused much time on applying these methods to chemical research.
In particular, they have explored how electrons become stimulated while forming chemical bonds.
As the electrons are stimulated they influence the properties of connected materials and molecules as well as subsequent chemical reactions.
The team published their initial findings in the paper, Quantum Simulation of Electronic Structure with Linear Depth and Connectivity.
In 2018, Google also launched Cirq, an open-source quantum computing framework.
This aims to allow developers and researchers the opportunity to explore the possibilities of quantum computing.
Developments in the Fields of Natural Science
The second and third fields of focus are Climate and Energy and Google Accelerated Science.
These are largely complementary, working alongside each other to further drive innovation.
These areas of focus seek to implement advances made in machine learning and AI in the field of natural science.
This sees researchers using AI to reduce harmful emissions, conduct biomedical research and enhance zero-carbon energy sources.
For example, by allowing AI systems to manage cooling systems at its massive data centers, Google has reduced energy use by 15%.
This is expected to be reduced further in the future as the system is further refined and improved.
In another example, Google AI, working alongside DeepMind, have implemented predictive AI systems at their American wind farm fields.
Here deep learning algorithms are trained on historical data sets to predict future weather patterns.
This information is fed to the local energy grid, allowing them to determine how best to use the energy.
This application will eventually see green technology, such as wind farms, which has been traditionally unpredictable become more useable.
Making Computer Tools More Widely Available
The fourth area of focus sees Google AI supplying scientific computing tools to other areas of Google.
Partner companies can also access these tools.
One of the most interesting developments is DeepDream.
This is a computer vision program.
Using a convolutional neural network it identifies and highlights patterns in images, turning them into dreamlike, highly processed images.
Its the ability to transform or augment images has made DeepDream a popular tool.
It also has applications in computer vision, image recognition and, even, art history.
Deepdream has also been the subject of its own art exhibition.
Backed by the Gray Area Foundation, a non-profit San Francisco based organization that promotes artistic and technological collaborations, a series of images created by DeepDream were put on public display.
Similarly, Google AI-powered cloud translate has been adopted by a number of companies. Bloomberg uses Google AI-driven automatic translation tools to keep customers updated in 40 different languages.
Meanwhile DPD a logistics company uses the tools to identify and process parcel information in a number of different languages.
This allows customer queries to be answered quickly and accurately.
Additionally, DPD is also utilizing Google Maps to improve driver delivery performance.
The overall aim of Google AI’s applied science department is to enhance both data and machine learning productivity.
The Google AI end-to-end Platform
Google AI is at the heart of the company’s aim to integrate and streamline its services.
This was highlighted at the 2019 Cloud Next conference.
Here, the company took the opportunity to showcase its many AI tools.
Google also revealed plans to democratize AI and machine learning by making available pre-built models and easily accessible services.
As well as making machine learning more available these services allow developers to build their own custom models and algorithms.
The key to this is the launch of the Google AI platform.

Still, only in its beta stage, the Google AI platform intends to provide an end-to-end service for developers and data scientists.
This allows users to easily build, test and implement models.
For this seamless integration to occur the platform brings together existing Google AI products as well as a new application.
This allows users to build a complete data pipeline, label the data and then exploit a classification service, object recognition or entity, extraction model.
Alternatively, users can employ tools such as Cloud Machine Learning Engine, or the simple to use AutoML.
These will allow users to train, test and finally deploy their custom-built model.
A Google AI spokesperson described the platform as the place to go to “if you are taking this terrifying journey from a journeyman idea of how you can use AI in your enterprise, all the way through launch and safe, reliable deployment.”
MORE – Data Science – 8 Powerful Applications
What is on the Google Platform?
As well as streamlining services the Google AI platform also houses a number of useful applications and systems.
For example, AI Hub allows users to easily discover, release and share machine learning models.
The Google AI Hub houses a catalog of reusable models that developers can access and easily use.
Amongst the catalog are models based on common frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow and Keras.
These can then be deployed in Kubeflow or deep learning VMs that are backed by TPUs or GPUs.
The Google AI platform Notebooks allow developers to create and manage pre-packed virtual machine instances.
The Google AI Notebook is synchronizable with Github, allowing for development, repetitive testing, and deployment to easily occur on a framework, such as TensorFlow or PyTorch.
The models generated can also be deployed on the Google AI Platform allowing for scalable hosting.
Google AI aims for its platform to support both batch and online predictions.
This platform is designed for developers and researchers.
However, it is also accessible for anyone else interested in machine learning and AI applications.
Similar Google Frameworks
The Google Platform is not Google AI’s only venture into this field.
The platform sits alongside TensorFlow.
This is a framework allowing users to build sophisticated deep learning and machine learning models, and Cloud ML Engine.
This latter platform is used for the purposes of training and deploying machine learning models.
Since 2017 Google AI has also been operating an open-source project called Kubeflow.
This aims to bring distributed machine learning to Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration system.
Kubernetes allows for the automating of application deployment, scaling, and management.
Kubeflow seeks to combine the best features of Kubernetes and TensorFlow.
This optimizes the processes of training and deploying machine learning models in containers.
By housing its deep learning, machine learning, AI systems, and platforms in one place Google offers an accessible, end-to-end service.
This means that the user can prepare data, train systems, tune and test algorithms, collaborate with other developers and deploy machine learning models in one place.

The Development of Google’s own AI Microchip
Chip development is a part of CEO Sundar Pichai’s intention to turn Google into an “AI-first” company.
This strategy will see the company cornering a significant part of the cloud-computing market.
The chip also reinforces Google AI’s long-stated belief that artificial intelligence is best improved by developing new hardware technology.
To this end, the second generation of Google’s microchip is focused on AI applications that require processing large masses of data.
The chip is known as a Tensor Processing Unit, or TPU.
Google AI hopes the TPU will set it apart from other cloud computing companies such as Amazon or IBM.

It is available for companies to rent via Google’s cloud computing service.
Unlike Intel or AMD, Google AI currently has no plans to sell its chip on the commercial market.
Deep learning and other associated techniques have made it easier for computers to carry out basic AI applications.
These include processes such as image recognition or language translation.
As AI becomes more widely used, the market concerned with developing technology is becoming more competitive.
Google AI hopes that by developing its own chip will help to place it ahead of the competition.
Already eBay is using Google AI cloud and associated technologies to improve its image search function.
Google also aims to democratize AI.
This means allowing the general public to access its endless possibilities.
FeiFei Li is the chief scientist of AI at Google’s cloud unit.
She explained that this aim motivated her to join the company, “to ensure everyone can leverage AI to innovate and stay competitive.”
TPU Applications
Google AI is already finding useful applications for its TPUs.
Jeff Dean is a co-founder of the Google AI Brain research team.
He revealed that TPUs had already enabled the company to reduce the time taken to train a language translation system.
By tethering multiple TPUs together the team had reduced the time taken from 24 hours down to just six.
Google AI’s TPU is able to perform two distinct AI-related tasks.
The first is the training of data, and the second is the process of making sense of the data.
This is known as inference.
The previous version of the chip was unable to do this task.
Unlike the TPU, other companies use separate GPUs to conduct this process.
The development of the TPU has seen Google AI stay true to the company’s stated aims.
With the hope of making AI accessible, and using artificial technology to find solutions to real-world problems Google plans to give the top machine learning researchers access to the TPUs.
Their access will be granted through a cloud computing service.
This service is intended specifically for academics researching AI capabilities and applications.
In return, researchers are required to publish their findings, making their research software available for others.
This information is published on a Google AI-powered open-source model.
With the hope of developing new treatments, Harvard Medical School has already signed up to use Google AI and deep learning tools.
The TensorFlow Framework
One of Google AI’s most widely used and versatile developments is TensorFlow.
An open-source library, TensorFlow aims to make machine learning faster, easier and more accessible.
TensorFlow has a number of different potential applications.
This means that it can be used in numerical computation and machine learning.
It also allows developers to create dataflow graphs.
A dataflow graph is a program model that has no conditionals.
In high-level programming, this means that there is only one entry point and one exit point.
A dataflow graph shows how data moves through each processing node in the code.
By using dataflow graphs developers can see the order of operation, helping to reduce potential issues or conflicts.
Developed by Google AI’s Brain Team, TensorFlow provides a framework in which developers can process data.
TensorFlow’s architecture also allows users to test and train models.

TensorFlow is a Versatile Framework
TensorFlow’s versatility means it runs on a number of applications such as cloud, iOS, Android, or GPUs.
Google AI has also developed the Tensor Processing Unit microchip, this customized way of running TensorFlow is designed to accelerate usage.
Models developed in TensorFlow can be used on any device.
Google AI’s TensorFlow allows abstraction to be used in machine learning.
This is one of its main benefits.
In short, it means that developers don’t have to spend time working out algorithms, the system is ready built.
The developer, instead, can focus their time on the logic of the application.
TensorFlow isn’t the only major framework in this area, PyTorch and CNTK are two other examples.
However, Google AI’s application has one main advantage over the competition.
TensorFlow is backed by Google, this means that it is convenient, easy to use and easily integrated with other applications.
TensorFlow is Increasingly Growing in Popularity
Programmers, Researchers, and data scientists, with TensorFlow, are all able to use the same toolset.
This allows for collaboration, work efficiency, and larger data sets to be created.
The larger the dataset an algorithm is trained on the more complex and capable it can become.
The Google AI Brain Team developed TensorFlow to fill the gap between researchers and product developers.
Increasingly academics, startups, and large companies are looking to exploit the potential of TensorFlow.
The US military uses TensorFlow for its ability to quickly analyze the large amounts of data gathered by their drones.
Since 2015 it has also been available for use by the general public.
This proved to be a popular decision.
Today, TensorFlow is the deep learning library with the most repositories on GitHub.
TensorFlow is also used in a number of common Google products, including Gmail, Photo and Google Search Engine.
How is TensorFlow being used?
As Google AI’s Brain Team has designed TensorFlow to be accessible and scalable it has already seen a number of different applications.
One main field is in the development of voice and sound recognition.
Developers have realized that with the correct input data feed, neural networks can understand audio signals.
This has already been applied, most commonly, in Google’s voice assistant.
Similarly, the technology drives voice search features in telecoms, sentiment analysis in customer relationship management and flaw detection.
This final application, commonly used in aviation and automotive, sees smart sensors detecting slight changes in engine noise.
When applied, for example, to oil drilling rigs the slightest change in noise can alert engineers to possible major issues.
By servicing the machine at this early point before it breaks downtime and money can be saved.
This process is commonly known as predictive maintenance.
MORE – 10 Applications of Machine Learning in Oil & Gas
Voice and Audio Recognition Applications
Tools powering voice and sound recognition are among the most commonly found uses of deep learning.
Similarly, text-based and text summarization applications such as Google Translate are driven by computer learning systems including TensorFlow.
Here TensorFlow works alongside other developments made by Google Ai and DeepMind.
Another Google-specific use case is the SmartReply feature found in Gmail.
This automatically generates email responses.
Improving Image Recognition
Face recognition, image search, machine vision, motion detection, and photo clustering all use forms of machine learning or deep learning.
These applications are used in a wide range of industries.
In the healthcare field, technology reads patient scans, detecting signs of disease.
In automotive development, image recognition is key to developing autonomous vehicles.
MORE – World’s Top 33 Companies Working on Self Driving Cars
Assisting Conservation Initiatives
Using Google AI’s TensorFlow for object recognition algorithms has a key advantage.
The framework helps users to classify and identify small or incidental objects in a large image.
In engineering, this application allows for shapes to be identified.
This aids modeling and allows for 3D space reconstruction using 2D images.
DeepMind, a Google-owned startup is using this ability to help with conservation efforts in the Serengeti.
Their application is able to read and label hundreds of images taken by field cameras placed all over the national park.
This allows conservationists to easily monitor animal numbers and movements without having to disturb their natural behavior.
Previously this work was done by volunteers, using internet sites such as Zooniverse.
However this was a time-consuming process, it could take up to a year for an image to be properly processed and labeled.
Google AI and DeepMind applications speed up this process significantly without sacrificing reliability.
A complex discipline, Google AI’s TensorFlow makes machine learning an accessible option for developers and amateurs.
This accessibility also means that more applications can be developed to power improvements in a wide range of fields.
Google is Increasingly Powered by AI
Increasingly AI applications are driving Google’s applications and services.
For example, Google’s all-encompassing search engine is now powered by AI applications.
Originally driven by algorithms that were set to automatically generate a response to an inquiry, this approach was restrictive.
The algorithms were constrained by a set of rules, which Google’s engineers could change and refine.
However, they didn’t learn on their own.
Google improved the search engine in a number of ways.
Incorporating neural networks and deep learning systems, as well as AI tools, Google created a responsive search engine capable of learning and adapting.

Google AI Applications
AI approaches are also behind Google Maps’ driving mode.
This is able to predict where you are going and helps you to navigate your way to your destination without a command.
In India, Pizza Hut is using Google Maps to optimize delivery times.
Google AI tools are also helping GO-JEK to navigate the congested streets of Jakarta.
Google Photos and its suggested image share function is a further example of AI powering Google features.
Another benefactor of Google AI developments is its Google Assistant feature.
Capable of searching for weather forecasts, recording shopping lists and setting reminders all these applications employ AI-driven tools.
Some reports even rate Google Assistant as more useful and reliable than Apple’s similar Siri feature.
This is partly because Google’s Assistant is more accessible, users can easily transfer from search results to related applications.
For example, if you search for the nearest restaurant, once the search results are returned you can seamlessly navigate to Google Maps to plan your route.
Google Assistant also has a form of short term memory, it is also able to remember what you’ve just said.
It can also tell jokes, recite, poetry and speak foreign languages.
These functions are all driven by Google AI applications.
Google AI – The Venture Capitalist
Google is not just working on its own AI projects.
The company is aware that there is a lot of research and development currently taking place in the field of AI.
With this in mind, and keen to not be left behind, Google is also investing significant sums of money as venture capital investment.
Through its various subsidiaries, Google has become a venture capital juggernaut.
In 2017 alone, it has invested in over 100 companies making it one of the largest ‘corporate’ investors.
Investing in Early Stage Projects
Formerly known as Google Ventures, GV is focused on investing in early-stage, often private projects.
Many of these projects compliment developments made by Google AI, such as DocuSign.
DocuSign is a world leader in the field of eSignature transaction management.
Others, such as Farmers Business Network, seek to use AI and real-time data to modernize farming and improve productivity.
Many of these investments have proved to be incredibly successful.
For example in the four months following their IPO, DocuSign’s shares rose in value by 83%.

Google is also Investing in Later Stage Companies
Capital G is Google AI and Alphabet’s growth equity investment fund.
Unlike GV, Capital G focuses its investments on larger technology companies, particularly those who are ready to grow.
Instead of focusing on companies that can help to develop Google AI, these investments are primarily focused on making money.
This investment not only helps the companies to grow, but they are also able to access Google AI-driven applications and knowledge.
Capital G has the freedom to invest in a range of operations.
As well as startups such as Oscar Health Insurance, Capital G has also invested in Snapchat.
However, Capital G also invests significantly in Ai related businesses such as Pindrop Security.
This is a startup that focuses on preventing phone fraud.
Capital G invested a significant sum, $75 million, in the business, aware of the growing importance of cybersecurity.

Gradient Ventures Dedicated AI Investments
Launched in 2017, Gradient Ventures focuses on making investments in AI startups.
In addition, Google AI engineers will be on hand to advise and ensure that investment is a success.
The intention is for Gradient to make 10-15 investments of up to $8 million dollars each year.
Anna Patterson, the managing partner explained that the purpose of this is to help speed up the development of AI.
“If we’re really going to help AI happen faster, we needed to be more involved in the community,” said Patterson.
It is this focus on AI, and how it can benefit other Google AI developments that set Gradient Ventures apart from other Google investment interests.

Visual Imaging Software to Monitor the Borders of the Future
One company that’s work complements work done by Google AI’s team is Cogniac.
Describing themselves as an enterprise platform, Cogniac aims to use AI to quickly and reliably automate visual tasks.
Cogniac’s image processing applications are already being used by the U.S. Army.
Here battlefield data harvested by drones can be quickly and accurately interpreted.
This application is currently being used to monitor people crossing the U.S. Mexico border.
It is thought that in the future this technology may help to form part of a virtual border wall.
Another investment, that links to Google AI’s work in the field of Natural language processing (NLP), translation and voice-activated assistants is Elsa.
Elsa is a mobile application that uses speech recognition applications to assist English learners with pronunciation.
Investing in Machine Learning and AI Applications
Gradient Ventures is focusing primarily on AI startups.
This has already seen major investments in companies such as Algorithmia, a platform automating the machine learning process.
The company also aims to provide accessible machine learning models, making algorithmic intelligence accessible and useful.
This has resulted in the company building the world’s biggest algorithm marketplace.
In 2018, Forbes reported that Algorithmia had a library of over 4,500 algorithms.
These are regularly being accessed by over 60,000 developers.
This links well into Google AI’s focus on open-source initiatives and applications.

Codename ‘X’ Investing in ‘moonshots’
Google has, since 2010, been investing in ‘moonshots’.
The investment is carried out by a secret research and development lab called “X”
These are imaginative projects designed to solve major problems and deliver outsized returns not normally associated with conventional investment funds.
Many of these projects seem unconventional or unlikely to succeed, hence the name moonshot.
However, they have given rise to a number of exciting innovations.
One of Google AI’s earliest moonshots was Google Glass.
While this was not a great success, Google has continued to work on the possibilities under the name Glass Enterprise Edition.
Here the focus is on manufacturing attachments for safety goggles or eye shields.
The intention is to allow workers to read instructions when they are operating tools or repairing large pieces of machinery.

Another Project X development is Project Loon.
This was initially conceived as a means of connecting people to the internet without using wires.
Instead, Project Loon makes use of a network of stratospheric balloons.
Not only has this initiative already helped to bring the internet to Kenya but it has also helped to keep people connected following natural disasters.
For example, following Hurricane Maria in 2018, Project Loon was utilized alongside AT&T and T-Mobile.
Here 30 balloons were flown over Puerto Rico, replacing destroyed telephone masts and enabling over 200,000 to get back online.
Google AI is Helping Google to Keep Innovating and Stay at the Forefront of Technology
Google has realized that artificial intelligence and machine learning can be used to drive further innovations and discoveries.
These developments can be given real-world applications.
In the fields of healthcare or scientific research, these applications can help to push discoveries or improve patient care.
These developments are also being used to improve Google’s own services.
As Google AI drives innovation, real-world applications of AI, deep learning and machine learning will become more commonplace.



















