
Computer vision, or abbreviated to CV, is an increasingly important technology in the field of artificial intelligence.
Those involved in its development believe that it has endless possibilities and a wealth of applications in a range of fields.
These include developing non-invasive health care treatments to self-driving vehicles and virtual shopping experiences.
Through the course of this article, we will seek to explain exactly what computer vision is and the applications of computer vision in all major industries.
We will also look at its current limitations as well as how it is already being applied.
Computer vision has the potential to transform a number of operations and sectors.
As it grows in importance, its potential and applications will be key to helping it enhance your organization.
Table of Contents
What is Computer Vision?
Computer vision is a branch of artificial intelligence that enables computers to see and identify images, processing them as humans would. Using images from cameras and videos, deep learning models enable machines to accurately identify and classify the objects.

How Does Computer Vision Work?
Computer vision can be confused with image processing. However, computer vision is a more high-level process. It deals with the analysis of an image. In the CV process, the input is an image while the output is the interpretation of an image. Computer vision works by identifying different components in the image.
These components are then analysed.
A simple application sees computer vision identifying the edges in an image.
Computer vision enables pattern recognition or shapes to be identified.
More advanced applications allow for animals or people to be recognised.
This application of CV is central to automated vehicles and drones as well as facial recognition and augmented reality software.
What are Computer Vision Applications?
Applications of computer vision range from automation in self-driving vehicles to developing accurate facial recognition software to inspecting bottles in a manufacturing production line to controlling robots, to organizing information for example indexing databases of images.
Computer vision, as well as AI and machine learning concepts, are key to realising complete, or Level 5, automation in self-driving vehicles.
Here CV software analyses data from cameras placed around the car.
This allows the car to identify other vehicles and pedestrians as well as reading road signs.
Computer vision is also key to developing accurate facial recognition software.
This is regularly being implemented by law enforcement agencies as well as helping to authenticate consumer device ownership.
Augmented and mixed reality technologies are increasingly being implemented in smartphones and tablets.
Additionally, smart glasses are also becoming more widely available.
All of this requires computer vision to help determine the location, detect objects and establish the depth or dimensions of the virtual world.
What are the Challenges of Computer Vision?
Computer vision is a challenging field of computer science.
Enabling a machine to be able to see, and process what it sees, like a human, is difficult.
Not least because we are still learning exactly how human vision works.
Firstly, for computer vision to succeed recognition must become robust.
This involves resolving issues such as object classification, identification, verification and detection.
Additionally, a successful CV system will be able to identify the key points or landmarks in a photograph.
Object segmentation, identifying the pixels in an image is also key to successful object recognition.
Once recognition is achieved CV systems must also correctly analyse the image.
If applied to a video, this requires accurate motion analysis.
This allows the system to estimate the velocity of objects in the video.
Other applications such as scene reconstruction, the creation of a 3D model via the inputting of 2D images or video, are also problematic.
These issues must all be resolved if computer vision is to continue growing in importance and value.
Computer Vision Applications in the Financial Sector
Computer Vision is already impacting on the banking and finance industry.
Mitek Systems develop computer vision-driven image recognition applications.
This allows for passports, driver’s license and ID cards to be accurately checked.
Mitek Systems applications allow customers to use their mobile device to take a photograph of their ID.
This can then be sent to the bank where CV software verifies the authenticity of the document.

Using CV systems to automate authentication helps to speed up identity checks.
This, in turn, speeds up business processes and financial transactions.
While images can often be rejected due to poor quality, Mitek Systems claims that their software is able to correct image faults.
Their algorithms correct common faults such as distortion or poor lighting.
Among Mitek Systems clients is the Mercantile Bank of Michigan.
They wanted to expand their retail portfolio and associated core deposits.
The bank identified that one way to do this was to provide clients with digital services.
The Mitek System’s Mobile Deposit application was implemented within a month.
Within four months 20% of online customers at the bank were using the application.
This application of computer vision is enabling customers to verify their identity in a quick and secure way.
By automating identification, human error is removed from the process.
While the convenience of simply scanning your ID means that transactions and checks can be carried out quickly and securely.
MORE – 10 Applications of Machine Learning in Finance
Computer Vision in Self-driving cars
It is thought that 20% of road accidents are caused by fatigue.
Around a quarter of these accidents often leave people involved with either serious injuries or result in fatalities.
Computer vision is helping vehicle manufacturers to combat this serious issue.
Waymo (a subsidiary of Google ) is in the process of attempting to optimise transportation.
To this end, they are equipping cars with cameras and CV systems, providing a 360-degree view around the car.
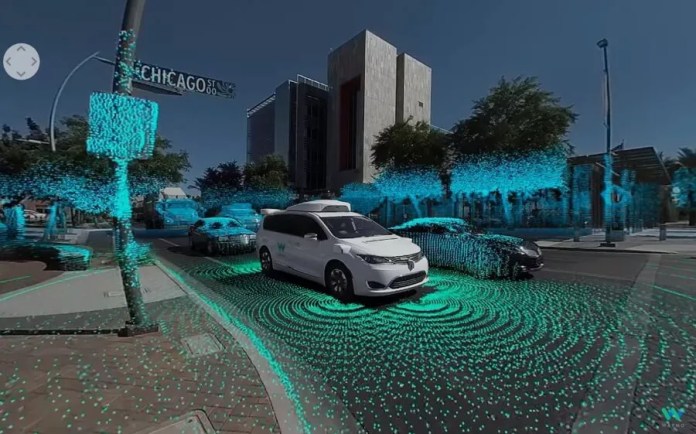

This system helps the vehicle to identify pedestrians from around 300 yards.
By spotting potential hazards early evasive action can be taken.
Fatigued drivers may be slower to identify and react to potential hazards.
Enabling the car to identify and react to these solutions can help to drive down accident rates.
Waymo is also using computer vision systems to train vehicles so that they can safely navigate through traffic.
This means that the car will be able to read temporary road signs and give way to oncoming emergency vehicles.
This application of computer vision sees it working alongside deep neural networks, enabling the car to safely navigate busy streets.
Dmitri Dolgoc is Waymo’s Chief Technology Officer and VP of Engineering.
He explained that “Raindrops and snowflakes can create a lot of noise in sensor data for a self-driving car. Machine learning helps us filter out that noise and correctly identify pedestrians, vehicles and more.”

Waymo is looking to apply this technology to public transport as well as private vehicles.
They have also partnered with Jaguar and Chrysler to continue developing automated vehicles.
MORE – World’s Top 33 Companies Working on Self Driving Cars
Tesla Vision
Similarly, Tesla is also using computer vision and deep learning on its Autopilot features.
This is the production of car models that are equipped for Level 5 or complete self-driving autonomy.
The Tesla Vision camera system sees vehicles being fitted with 8 cameras.
This provides 360-degree visibility at a distance of 250 meters.

The system also includes ultrasonic sensors, allowing the car to detect both hard and soft objects.
Additionally, Tesla’s forward-facing radar allows the car to see despite hazardous weather conditions such as heavy rain or fog.
This radar also enables the car to see through the car in front of it.

Computer vision systems are becoming increasingly common in vehicles.
Powering safety features such as obstacle detection as well as enabling driver risk assessment to take place.
In time CV will also help Level 5 automation, or full automation, to be realised.
Computer Vision to Diagnose Disease
Computer vision is being used to help diagnose health conditions.
This is enabling lifesaving interventions to be made. When used alongside sensors, smart healthcare becomes a reality.
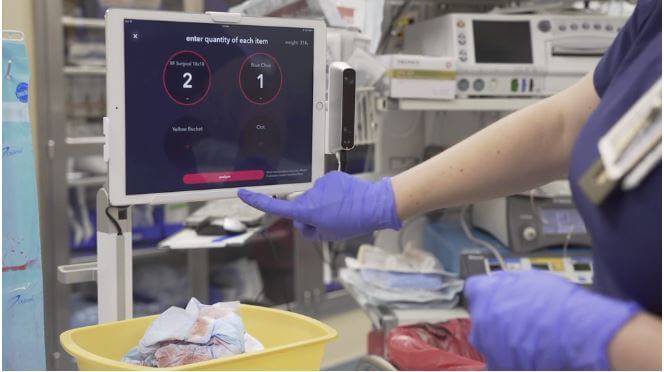
For example, Gauss Surgical has developed a solution that can monitor blood loss in real-time through the use of sophisticated cloud-based computer vision algorithms.

Their solutions are able to maximise blood transfusions. It can also recognise haemorrhaging better than a trained human.
This application is already being used in surgical operations such as Cesarean deliveries.
An Accuracy of Blood Loss Measurement during Cesarean Delivery study was conducted at the Santa Clara Valley Medical Centre in 2017.
This study revealed that its results were more accurate than visual estimates made by trained and experienced physicians.
Accurately measuring blood loss enables clinical outcomes to be improved.
This application of sophisticated tool will, therefore, help to improve medical and surgical procedures.
Open Source Solutions Enable Innovation
DeepLens is a deep-learning, computer vision hardware and applications developed by Amazon Web Services.
An open-source system, DeepLens can be adapted to power various applications.
One such development is DermLens.
This was developed by Predictably Well, a digital health startup.
DermLens helps patients monitor and manage skin conditions such as psoriasis.
A Journal of American Dermatology revealed DermLens was preferred to other monitoring solutions by 72% of users.
MORE – Top 10 Ways Artificial Intelligence is Impacting Healthcare
MORE – Artificial Intelligence in Medicine – Top 10 Applications
Assisting in Diagnostics
Computer vision can also help to identify and detect disease at its earliest stage.
The ChironX applications uses CV to read retinal fundus images.
With the help of deep learning, the system is able to detect eye disease at its earliest stage.
It is also able to predict the risk of eye disease and systemic diseases such as cardiovascular ailments from occurring.
This application of CV is not only accurate, but it is also cost-effective and non-invasive.
Consequently, patients can be diagnosed more easily and reliably.
This means that medical intervention can begin soon, helping to save sight or lives.
MORE – DeepMind: Behind the Scenes at a Trailblazing AI Startup
Computer Vision in the Retail Industry
Amazon is leading the way in developing technology for retail.
Recently the company unveiled a smart store, Amazon Go.
Here deep learning, CV and other sophisticated tools allow customers to pay for goods without the need for a checkout.

Amazon is not the only tech giant launching checkout less store, the Chinese internet giant Lenovo has also jumped onto the bandwagon.
Instead, CV powered facial recognition cameras monitor when items are taken from shelves and placed in carts.
By tracking a customer as they walk around the store, CV systems record every item a customer selects.
Then, when they have completed their shop, the customer simply leaves the store.
The technology present in the store is able to link the customer to their amazon account meaning that they are automatically billed for their purchases.
This application of sophisticated technology makes the need for cashiers largely redundant.
However, reports reveal that employees are still present in Amazon Go stores to check ID, stock shelves and assist customers.
Staff at Amazon Go stores also work behind the scenes, training algorithms if they incorrectly identify which item has been removed from the shelf.
MORE – 10 Powerful Applications of AI in Retail
Identifying Valued Customers
Retailer Lolli & Pops use computer vision-driven facial recognition software to identify valued customers the moment they enter a store.
An integrated app then informs the sales associate of the customers purchasing history, preferences and other potentially valuable information.
This application of AI-driven analytics helps to deliver a personalised service.

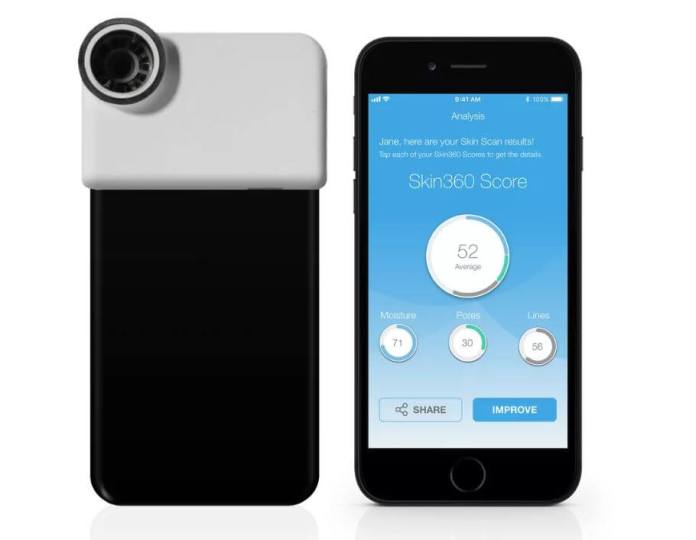
Similarly, Neutrogena uses an app to scan customers skin.
The Skin360 app then determines the health of the customer helping them to identify the most relevant or beneficial products.
These are just some of the ways in which CV and sophisticated tools are helping to personalise the customer experience.
Brands are increasingly aware that by providing a personal, tailored service customers are more likely to be satisfied and remain loyal and engaged with the brand.
This helps to maintain a strong customer base, which is the key to any business.

Reducing In-store Theft
StopLift is using computer vision to power systems that can help stores reduce theft and other losses.
Their ScanItAll system detects checkout errors and also identifies cashiers who avoid scanning products.
ScanItAll can also be easily installed into the stores existing video cameras and point of sale systems, making integration easy.
StopLift applications are already operating in stores in Massachusetts, Rhode Island and Australia.
A case study at Piggly Wiggly revealed that StopLift helped to significantly cut losses.
Industrial Applications of Computer Vision
Computer vision software is proving useful in helping to monitor the functionality of industrial sites such as wells or factories.
Osprey Informatics use CV to monitor remote wells, industrial facilities and site security.
Their systems are capable of providing regular 15-minute images from the site. They also provide real-time or live video monitoring.
This application helps to cut employee costs, and save time by optimising supervision processes.

One case study revealed that a client utilised the Osprey monitoring systems for remote oil wells.
This helped to reduce site visits by 50% as well as costs, helping the client to save money in a time of depressed commodity prices.
Osprey Informatics systems are already being used by large companies with complicated or large infrastructure bases such as Chevron and Shell.
Predictive Maintenance
Computer vision and sensors are also increasingly being used to monitor the health of the critical infrastructure.
Should a critical plant or tool, such as a drill, fail delays can be costly and lengthy as engineers make repairs.

This also creates a backlog, causing productivity to fall.
By using CV, sensors and other sophisticated tools to monitor the health and productivity of infrastructure faults can be identified and remedied early.
This is known as predictive maintenance, and it can save companies both time and money.
Many oil and gas producers such as Shell are using predictive maintenance to keep their equipment in prime condition.
As sensors and CV software become more sensitive this application will only grow in value.
MORE – 10 Applications of Machine Learning in Oil & Gas
Computer Vision Automating Inventory Management
Computer vision is increasingly being used for in-store inventory tracking.
For example, Walmart is expanding the use of Bossa Nova Robotics shelf-scanning robots to 350 of their stores.

These robots are able to identify products with missing labels as well as items that are out of stock or incorrectly priced.
CV enables this process to take place while also helping the robots to safely navigate the stores without bumping into customers.
With a similar aim in mind, Target has trailed the Simbe Robotics Tally robot in their stores.

Warehouse Management
Warehouse inventory management can be a complicated, time-consuming task.
This is particularly the case in large or busy warehouses that are operational for large periods of the day.
Gather AI is a Pittsburgh based company. They are developing autonomous drones to conduct warehouse inventory management.
These operate autonomously and are able to integrate with existing warehouse management systems and devices such as motion sensors.

CV systems then scan the recorded images, allowing for an accurate record of available inventory to be created.
Gather claims that this approach is around 60% cheaper than traditional management methods.
Gather systems are currently operating in a number of undisclosed warehouses.
In one warehouse, run by an air cargo company, the Gather system was able to reduce the time it takes an inventory check to be completed from 8 hours to 15 minutes.
Similarly, Amazon is introducing the Pegasus sorting robot into their warehouses.
The company sees this as the first step to complete warehouse automation.
Complete automation, they predict, will be achieved within a decade.

Helping Business to Optimise Marketing
Computer vision may still be evolving, this hasn’t stopped it from already revolutionising marketing with artificial intelligence.
One of the biggest challenges for any online marketing campaign is generating new content.
Generative Adversarial Networks are neural networks that are making this process a lot easier.
GANs utilise AI tools such as CV applications to help the user to create realistic visual content.
Japanese technology company ModelingCafe has used this application to create lifelike images of created fashion models.

Branded Object Recognition
Computer vision and image detection allow brands to monitor online channels such as social media platforms.
Here they can identify threats to their market dominance, such as an emerging, popular product.
This is known as social listening and it can also be used to help a brand to grow its own influence or maintain a good reputation.
Companies such as Gumgum use computer vision to identify brand logos.
Their automated searches then scan the internet looking for good and bad reviews.
This helps a brand generate valuable insights into product reception and customer interaction.
Their applications are being used by a range of global brands such as Adidas, Ford and the Bank of America.
Recently GumGum partnered with the New Orleans Saints and New Orleans Pelicans.
The aim of this partnership is to help the two sports teams better understand how far their media is reaching, and across which channels.

As social media continues to grow in importance both brands and sports teams are realising that they need to fully understand the reach of their influence.
This can help them to better engage with supporters.
Additionally understanding the reach of a brand helps to bring accountability to the sponsors of the team.
This can help to justify an increase in investment or product placement.
Visual Product Searching
When shopping online, most people use the search bar or the filter feature to sift through available products.
For this to function effectively a retailer must assign each product with a range of tags.
There is no standard procedure for tagging products, this means the search terms required to find the same product will vary between websites.
This can be confusing for customers, especially if they are unfamiliar with technical terms.

Pinterest has used computer vision and AI tools to develop Visual Search.
This enables visual product discovery, simplifying the product search process and eliminating the need for tags.
The user simply selects an image of a product that interests them.
They are then taken to a range of similar products, allowing them to browse their options easily.

Disney Monitoring Consumer Reaction to movies
Similar computer vision systems are helping businesses to track the focus and emotions of a customer.
For example, Disney developed systems uses infrared captures to record people’s response while watching a film.

Computer vision systems and machine learning algorithms can identify complicated facial clues.
This helps Disney to understand what element of the film provokes which emotion.
Consequently, Disney can predict how you’ll react to a movie before you even sit down to watch it.
This application can be applied to a range of businesses and services.
For businesses understanding the emotions and attention of a customer can help to predict sales revenues and gauge foot traffic.
If you believe that brand engagement is about to fall you can alter or devise a new marketing strategy to combat this.

Virtual shopping with computer vision technology
Amazon is using augmented reality and sophisticated tools to develop a virtual mirror.
Powered by computer vision tools this mirror displays an image of the customer onto which virtual clothing can be placed.
Facial detection software tracks eye movement allowing the software to understand what the user is looking at.
This application of computer vision follows on from the Amazon Echo Look.
Echo Look is a voice-activated camera that is designed to take photographs and short videos of the user’s wardrobe.
Algorithms process this information before suggesting outfit combinations.
Similarly, Sephora uses augmented reality and AI alongside CV and sophisticated tools to provide consumers with a virtual shopping experience.
The Sephora Virtual Artists allows customers to experiment with makeup shades and products.
This allows customers to try out new looks before they make an investment.

Additionally, Sephora also uses AI and smart tools to help customers find the perfect shade or product for their skin tone.
This is done simply by uploading a photograph to the app.
Simple services and solutions such as this help the customer to feel and look good.
They also help to keep customers engaged with products. This helps to maintain their relationship with the brand and helping to boost the business’s client base.
MORE – How Leading Retailers Like Sephora are Utilizing AI to Keep Stores Alive
Optimising Agriculture with Computer Vision
Increasingly farmers are looking to AI and sophisticated technology to optimise their operations.
Technology is already helping farmers identify the most efficient growing method, increase yield and reduce waste.
Computer vision is one such tool that is already making an impact.
SlantRange is just one company using computer vision to increase productivity.
SlantRange is mounting CV enabled cameras onto drones. These are then used to scan crops.

The gathered information is then fed into the SlantView analytic system.
From here farmers can derive insights such as whether or not they are under immediate threat of infestation or are lacking in water or nutrients.
SlantRange’s systems are also able to predict when a crop will be ready to harvest. in great depth for readers with a more general interest in that area.
Alex Petersen, the owner of On Target Imaging, used the SlantView system to analyse his farming methods.
SlantView reportedly helped him to identify areas where less fertilizer was required.
This alone helped him to cut costs. Utilising SlantView also helped him to increase productivity and profitability.
Crop and Livestock Monitoring
Healthy crops and livestock are vital for any farm.
Dublin based Cainthus is using sophisticated technology to help farmers monitor the health of their crops and livestock.
With CV and predictive image analysis, they have developed a system that is able to identify an individual cow.
Once identified the system can then monitor key information such as the animal’s food and water intake or their behaviour patterns.
AI-driven algorithms process this information, automatically warning the farmer is a problem is detected.
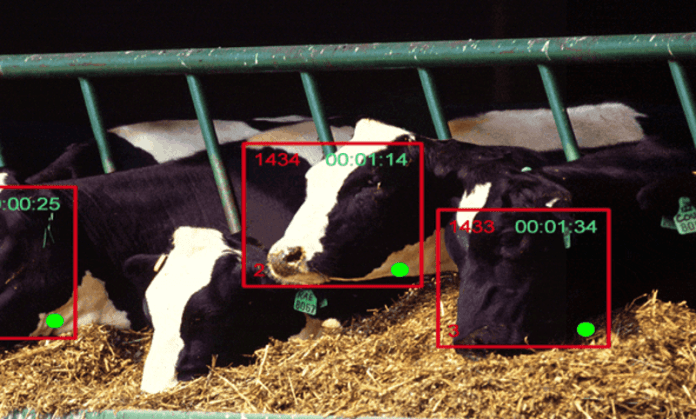

Similar Cainthus systems provide all-weather crop analysis.
This monitors not only the health of the plant but also its rate of growth and predicts when it is likely to ripen.
Information like this is valuable in helping farmers determine the prime harvest time.
In 2018 Cainthus entered into a partnership with Cargill, an agricultural products producer and distributor.
Together they are working on translating the Cainthus system into applications that monitor the health and activity of pigs and poultry.
Monitoring Conservation Efforts
Researchers at Caltech, the California Institute of Technology are using camera trap datasets to develop a CV model that can identify animals.
Conservation teams use camera traps to monitor animal behaviour and numbers in remote or wild areas.
However, camera traps produce lots of raw images.
Processing each image, and identifying the animals in it, can be a long and time-consuming task.
Computer vision can help to speed up this process while also improving reliability.
WildTrack is using CV, machine learning and sophisticated algorithms in a similar way.
The WildTrack Footprint Identification Technique is a sophisticated non-invasive tool.
It allows endangered species to be monitored by processing digital images of their footprints.
Measurements taken from these images can identify not only the species but also the sex and age-class of the animal.
This helps WildTrack to monitor endangered species such as the cheetah, an animal which has suffered a 93% decline during the past century.
By using computer vision-enabled camera traps, footprint ID and AI WildTrack are able to monitor the behaviour and population levels of the cheetah.
Encouraging Citizen Scientists
Crowdsourcing programs such as iNaturalist are also benefiting from this application of computer vision.
iNaturalist encourages people to use their mobile phone to take pictures of flora and fauna.
Machine learning classifiers and computer vision help the photographer to identify the species in their photograph by suggesting matches.
These images are then submitted to iNaturalists where biologists can process them quickly and usefully.
Similarly organisations such as Wild Me and their Wildbook platform utilising social media to improve scientific understanding.
For example, their whaleshark.org site.
At 10 pm every night, an intelligent agent linked to the site searches social media platforms for images of whale sharks.
Computer vision and sophisticated tools enable this search to be automatically and accurately performed.
These tools also help to identify different species of shark, helping to track the migration pattern of a particular animal, as well as the general health of the species.
Assisting Law Enforcement
The role of computer vision is law enforcement may not be widely recognised.
However, it is steadily growing in both usage and importance.
The IEEE reports that over 70% of the United States police departments use licence plate detectors.
This helps to identify drivers with suspended licenses, catch stolen vehicles or issue traffic citations.
It is not possible without the help of computer vision-driven software.
Similar systems are also being used to help law enforcement officers identify wanted criminals.
Over half of Americans have their driver’s licence photograph recorded on a national database.
This means that if the police have an image of a suspect, they can search the database of licences to identify the best matches.
As computer vision systems and machine learning continue to improve this application will only become more reliable.
It will also mean that blurry or less than perfect images, such as those taken from CCTV footage, can be used to identify potential suspects.
MORE – What are the Risks and Rewards Using AI to Detect Crime?
Body Cameras
Seattle based company Axon is better known under their previous guide of Taser International.
The company is best known for manufacturing the taser devices that police officers are regularly issued with.

However, Axon, as they are now known, are also developing other technologies.
The company is also producing computer vision-enabled body cameras.
Axon has offered every police officer in America the opportunity to wear one of their free body cameras.
These will provide the company with a never-ending data stream, enabling them to train more AI and sophisticated algorithms for crime-fighting applications.
Soon these cameras it is thought will be able to help identify criminal suspects in real-time.

This will be done by video streaming what the camera sees into computer vision-driven servers based at Axons headquarters.
In the future, Axon is working towards training an algorithm to predict whether somebody may, one day, become a criminal.
Computer Vision Provides an Insight into the Future
Computer vision implementation is increasingly common.
As systems prove and the technology continues to develop and prove its worth this adoption will only increase.
In addition to helping the automation of vehicles, computer vision will allow stores to operate with minimal human intervention.
Applications of computer vision will also help to improve business operations, assist in conservation and law enforcement efforts and improve health care.



















