
Big data is becoming increasingly important for businesses and organisations.
An IDC forecast suggests that by the year 2022 the worldwide revenue for data and analytic solutions will reach $260 billion.
As it grows in relevance more companies and organisations are seeking to unlock its potential.
However, like many innovations, this will only benefit you if you properly understand it and its capabilities.
Through the course of this article, we will explore what big data is, and why it is so useful.
We will also look at how different businesses and organisations are using it to transform their processes.
This will give you valuable insight into data applications and how you can use it to optimise your business.
Table of Contents
What is Big Data?
Simply put, this is a term that describes the large volumes of data that a business deals with on a daily basis.
According to Gartner, it can be defined as “high-volume, velocity, and variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing for enhanced insight and decision making.”
Big data analytics allows businesses to process this data or information.
Properly processed this provides valuable insights.
These can help a business to cut costs, increase customer interaction with a brand or grow their operation.
These terms are relatively new. However, the process of gathering data on customers or business operations, and using it to improve and develop strategies is not new.
Why Is Big Data Important?
Big data is increasingly growing in importance. Used alongside high powered analytics allows a business to gain valuable insights. These insights can be used to develop and modernise, improve strategies and refine processes.
However, the amount of data you have isn’t as important as what you do with it.
Data from any source, if properly analysed, can be used to cut costs, save time, optimise processes, develop new products or make informed decisions.
Rich in potential, the importance of this area is only going to increase in the coming years.

Big Data Characteristics
Big data characteristics can be defined by one or more of these three characteristics:
- A massive amount of data that is quick growing
- Data that grows so quickly in volume it can’t be processed with conventional means
- The mining, storage, analysis, sharing and visualisation of data.
Its term can also include data frameworks as well as any tools or techniques employed to analyse the data
Data can be structured, unstructured or semi-structured.
Structured data is highly organised. Coming in a fixed format it is easy to process, store and access.
Semi-structured data is a data set that holds both structured and unstructured pieces.
This form of data hasn’t been classified in a database.
However, it still contains vital information that segregates elements in the data set.
Unstructured data lacks any set form or structure.
This makes accessing, processing and analysing it a time consuming, and difficult task.
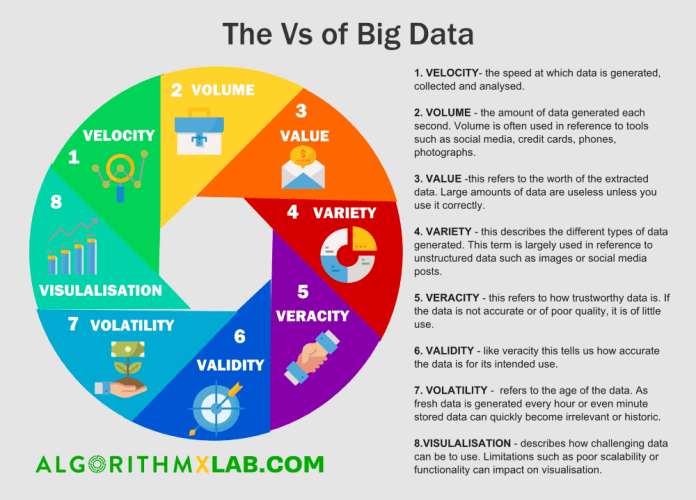
The Vs of Big Data
Big data is often characterized by Vs.
These are:
- Velocity, the speed at which data is generated, collected and analyzed.
- Volume, the amount of data generated each second. Volume is often used in reference to tools such as social media, credit cards, phones, photographs.
- Value, this refers to the worth of the extracted data. Large amounts of data are useless unless you use it correctly.
- Variety, this describes the different types of data generated. This term is largely used in reference to unstructured data such as images or social media posts.
- Veracity, this refers to how trustworthy data is. If the data is not accurate or of poor quality, it is of little use.
- Validity, like veracity this tells us how accurate the data is for its intended use.
- Volatility refers to the age of the data. As fresh data is generated every hour or even minute stored data can quickly become irrelevant or historic. Volatility also refers to how long data needs to be kept before it can be discarded or archived.
- Visualisation describes how challenging data can be to use. Limitations such as poor scalability or functionality can impact on visualization. Additionally, data sets can be large and vast. This makes it complicated to use or visualize in a meaningful way.
How Big Data is Stored and Processed
Big data is stored in a specifically designed storage infrastructure.
This infrastructure makes managing and retrieving information easier.
It also requires data to be stored correctly.
This makes it easier to access, use and process.
Typically storage is comprised of redundant and scalable direct-attached storage pools and clustered network-attached storage.
Connecting the storage infrastructure to computing server nodes makes processing and retrieval of data quick and easy.
Storage is also designed to be flexible. This makes scaling it easier.
Finally, most data storage options are able to support data analytic solutions.
One of the most established methods of processing big data is Apache Lucene.
Initially, Lucene was developed as a full-text, downloadable search library.
Since 2002 it’s processing and storage components have also been applied to Hadoop.
Hadoop is a collection of open-source procedures and programs.
Free to use and adapt, these form the spine of many data operations.
Other Big Data Storing and Processing Options
Another popular system for processing big data is Spark.
A superior memory to other systems means that it can quickly process data.
Its compatibility with Hadoop also helps it to work quickly and efficiently.
Spark also runs as a standalone processing engine.
The Apache Flink engine is capable of processing high volume data streams.
Its Complex Event Processing library allows users to design the search conditions of a data sequence.
The user is also able to alter the sequence of events.
Another processing system is Apache Storm.
This is designed to make processing data easy and possible in real-time computation systems.
Highly scalable it is able to process over a million tuples a second.
Apache Samza is also capable of processing distributed data streams.
Incorporating Apache Kafka, Samza guarantees that processed messages are dealt with in the order that they are received.
This ensures that no messages, or data points, are lost.
Consequently, Samza creates ordered, replayable, fault-tolerant, partitioned streams.
Additionally, by utilising YARN, Samza has a pluggable API.
This allows it to work with other messaging systems.
Challenges Faced When Dealing With Big Data
There are a number of challenges when dealing with big data.
The most common is that many companies implement data strategies without first doing any proper preparation.
This means that projects often stall, or return no useful results.
A 2017 survey by NewVantage Partners Big Data Executive revealed that 95% of Fortune 1000 business leaders surveyed had begun a data project in their firm.
However less than half of these projects had achieved a measurable result.
In order for big data to be effective, it must be properly understood and processed.
For this to occur firms must have a clear goal in mind before attempting to unlock the power of data.
Proper frameworks and methods must also be put in place. They must also recruit staff with the correct level of understanding.
Other Big Data Challenges
Dealing with data growth can also pose difficulties.
A Digital Universe report by IDC estimated that the amount of data stored in IT systems doubles every 2 years.
Increasingly this data is unstructured. Unstructured data is time-consuming to organise.
It can also be difficult to store and process.
The new generation of ETL and analytics tools are helping to reduce the time it takes to generate reports.
Eventually, we will be able to generate real-time reports however this is not yet possible.
Another consequence of data being unstructured, or coming in a variety of forms, means that validation can be problematic.
Data governance is the process of getting data in different forms to agree.
It also ensures that the data is accurate and useable.
A 2016 Big Data Maturity Survey by AtScale revealed that proper data governance was a growing area of concern.
Securing data is another growing challenge. Increasingly data is a target for advanced persistent threats and hackers.
Securing data, particularly sensitive information such as clients banking information, is a vital concern for organisations.
The Big Data Skills Gap
Big data is still an emerging sector. This means that there aren’t enough skilled experts to meet the demand.
Currently, organisations can struggle to recruit, or train people to fulfil this role.
Consequently, experts are highly valued.
In 2017 the Robert Half Technology Salary Guide reported that data engineers were earning on average $135,000 and $196,000.
This reflects not only the skills required to do the job but the demand in which data engineers are currently held.
Big Data Collection Practises and Regulations
Collecting data, particularly customer information, can help a business to optimise its performance, products and marketing strategies.
However, there are concerns over how this information is gathered and used.
The General Data Protection Regulation came into effect in the European Union in 2018.
This regulation places more emphasis than ever on data analysts and users to act responsibly.
GDPR requires companies to properly store and protect any data they harvest.
Companies are also required to only harvest data via legal methods and must inform each individual potentially concerned if there is a data breach.
The GDPR gives EU residents control over their data, including the right to erase portions or complete data sets.
David Carroll is an associate professor at the noted New York’s Parsons School of Design.
He explained that “Marketers have succeeded in making people feel powerless and resigned to getting the short end of the bargain. GDPR gives consumers the chance to renegotiate that very unfair deal.”
While GDPR applies only to people located in the EU it will also serve to pressurise companies in other parts of the world to act with the same degree of responsibility.
For example, following the introduction of GDPR Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg praised the regulation.
He also announced plans to offer similar controls to Facebook users all over the world.
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big data analytics is the process of examining large or varied data sets.
It allows us to identify patterns, correlations, trends and other pieces of useful information in data sets.
A form of advanced analytics, this process uses complex applications including statistical algorithms and predictive models to analyse data sets.
In a wider sense, data analytics technologies and techniques are tools that help to analyse data sets.
These tools can also turn information in data sets into an understandable and accessible form.
This makes the information useful for businesses.
The Importance of Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics can benefit businesses in a number of ways.
These include:
- Identifying new revenue streams and opportunities,
- Helping to devise more effective marketing campaigns,
- Improving customer service,
- Improving and streamlining operations, allowing businesses to become more efficient.
Properly implemented analytics can help an organisation to gain a competitive advantage over rival companies.
Big Data Analytics Technologies and Tools
Big data is often unstructured or semi-structured.
This means that it doesn’t fit well into conventional data repositories.
In order to properly and fully harness the potential of big data, various tools and technologies must be used.
These include the cluster management solution YARN and MapReduce, a software framework allowing users to process data sets.
Processing frameworks such as Spark are also key to effectively using big data.
Other tools such as Hive, a data warehouse system for analysing data sets, and the messaging system Kafka are also regularly used.
How Big Data Analytics Works
Frequently data analysts are using data lakes to serve as a primary repository.
Here raw data is processed and analysed in either Hadoop clusters or run through processing engines like Spark.
Correctly processing the data here is key to getting the most out of it later on.
Once processed data is stored, organised, configured and partitioned.
Following this, the data can be used in data mining processes, for predictive analytics or to program machine learning or deep learning algorithms
Big Data Analytics Uses and Challenges
Big data analytics allows data to be used in a range of forms.
It is proving to be particularly useful in improving processes such as supply chain analytics.
In this scenario the insights provided by big data analytics allows for more informed, and more effective, decisions to be made.
This, in turn, can streamline and enhance the supply chain process.
Like big data, analytics faces a number of problems.
These include the correct processing and storage of data sets.
Both of these are vital for the information to be easily and properly accessed and used.
Privacy concerns are also pressing.
Data sets can often be a target for hackers and malicious attacks.
Finally as big data analytics is still an emerging field it can be difficult or costly for organisations to recruit experienced data scientists and engineers.
This gap in the skills base means that many companies can struggle to harness the potential of big data.
How is Big Data Used?
As we will see from the following case examples, big data and analytics have a number of useful applications.
These include general-purpose applications that can be applied to a range of businesses in many sectors.
These applications allow for a better understanding and targeting of customers or optimising business processes.
Big data also has more specific applications such as improving patient care, optimising supply chain management and helping in the quest to develop fully self-driving cars.
Big Data in Banking and Finance
Big data has a few clear benefits if applied successfully in the banking industry.
Firstly, as in other business applications, it allows for a full overview of the business to be made.
Big data allows the user to easily see customer behavioural patterns and market trends.
Secondly, big data allows you to monitor the efficiency of internal processes.
In conjunction with AI and machine learning applications, this allows you to optimise performance and reduce costs.
A third application allows users to employ intelligent algorithms, improving cybersecurity and detecting fraud or malicious actions.
READ – 10 Applications of Machine Learning in Finance

Personalising the Banking Experience
Oracle reports that 84% of surveyed executives agree that their customers appreciate a personalised experience.
Big data allows banks, and businesses, to get to know their customers.
American Express is using this approach in their Australian branches.
Here sophisticated predictive models analyse over 100 variables including previous transactions.
The information is then used to forecast customer churn.
This allows the company to target customers at risk of leaving and encourage them to re-engage.
Banks are also using big data to improve segmentation and targeting, especially in the field of marketing.
Mckinsey reports that it can help to optimise marketing strategies, saving up to 20% of your budget.
On average a bank spends 8% of its overall budget on marketing.
Using data to optimise their marketing strategies will help to save banks money.
It will also help to generate more customers and increase revenue.
Using Big Data to Listen to Customers
Barclays bank is using sentiment analysis under the name “social listening”.
This process allows the bank to identify insights from social network users.
An obvious example of using this process to improve customer satisfaction came with the launch of Pingit.
Designed by Barclays this is a money sending, mobile app.
When it was first launched the bank monitored its reception on social media.
Analysis of the data revealed people complaining that users under the age of 18 couldn’t use the app to transfer or receive money.
Barclays was able to quickly identify this problem and resolved the issue. This means users over the age of 16 were able to access all the apps features.

Banking on Automation
Research by Mckinsey suggests that 30% of bank work can be automated.
Much of this automation will rely on the successful implementation of big data.
JP Morgan Chase is pioneering automation in the banking industry.

This drive to innovate has seen the company use AI and machine learning programs, optimising processes such as loan agreements.
One of JP Morgan Chases’ programs is LOXM.
This uses historical data, from billions of transactions, allowing the company to trade equities “at maximum speed and at optimal prices”.
Automating trading has made the process more efficient and helped the company to reduce expenditure.
MORE – Top 50 RPA Tools & Software – A Comprehensive Guide
MORE – RPA – 10 Powerful Examples in Enterprise
MORE – Essential Enterprise AI Companies Landscape
Making Banking Safer
As well as optimizing their processes JP Morgan Chase is also using big data and AI to identify potential fraud.
This application sees systems processing large amounts of data to identify behavioral patterns that suggest a potential risk.
CitiBank has also identified the potential of data-driven technology.
Under the Citi Ventures initiative, CitiBank is investing in startups and partnering with tech companies.
The main focus of this initiative is in the field of cybersecurity.

With this end in mind, CitiBank chose to invest in data science company Feedzai.
They have developed a real-time machine learning and predictive modelling system.
This uses data analysis to identify potentially fraudulent behaviour such as unusual charges.
As we can see from these examples, data can help to cut fraud and minimise financial risks, especially in online banking.
BNP Paribas is a global banking provider. They are using data analysis to improve branch productivity.
This application allows branch managers and chief executives to access an accurate overview of a branch’s performance.
Managers are able to easily access an overview.
This includes a range of factors such as turnover, employee efficiency and customer acquisition.
Using this system allows BNP Paribas to quickly identify and resolve problems in real-time.
AI Revolution Disrupts Investment Banking
Providing Insights into Financial Markets
High-Frequency Trading, or HFT, is an area prime for big data optimisation.
This sees algorithms analysing a range of factors such as news websites, social media networks to help make trade decisions.
Quantitative analysis is increasingly being used in favor of older, manual trading strategies.
China Fund is just one trading group using big data in its quantitative research.
This application allows investors to get a clear picture of the Chinese market.
The more informed an investor is, the better the decision they will make.
This is particularly useful in riskier markets such as China.
Prior to this, investors, not understanding the subtleties of the market, were often reluctant to invest.
This application of data analysis is opening the market up to more investors.
Big Data in Risk Management
A robust risk management plan is vital for any business.
It helps to see potential risks, mitigating events before they become critical.
This allows a business to remain operational and profitable.
Big data analytics has been instrument helping to evolve risk management solutions.

Thanks to analytics businesses are able to increase the statistics they harvest.
This wealth of information means that a business is better able to model potential risks, improving its risk management strategy.
Singapore’s UOB bank is just one business that has used analytics to improve its risk management.
A financial institution, a poorly conceived risk management strategy has the potential to cost UOB billions of dollars.
Big data risk management systems enable the bank to accurately and quickly evaluate potential risks.
As systems continue to improve this analysis may be able to be carried out in real-time.
How Banks Can Start Using Machine Learning?
AI in Banking – A Look at the Top 5 Banks in the US
Big Data and Improving Patient Care
The healthcare sector is proving one of the most proactive in the adoption of big data applications.
Sepsis is an extremely serious condition that can cause serious injuries.
In the U.S. alone it is responsible for the deaths of around a quarter of a million people every year.
If caught early enough sepsis is treatable. However, it is very hard to identify.

Dignity Health, the largest hospital provider in California is using advanced data analytics to predict potential sepsis cases sepsis.
Their Sepsis Bio-Surveillance Program helps the company to monitor 120,000 patients across 24 hospitals every month.
Using a rules engine and NLP this program constantly monitors patients for factors that may indicate sepsis.
If the condition is detected the primary nurse or physician is alerted.
28 of the hospitals using the Sepsis Bio-Surveillance Program reported an average decline in sepsis mortality rates of 5%.
This also helps save hospitals money because patients are spending less time in intensive care.
DeepMind: Behind the Scenes at the Hottest AI Startup in Healthcare
Top 10 Ways Artificial Intelligence is Impacting Healthcare
Using Data to Improve Treatment Plans
This or similar applications of big data can be used in other forms of medicine.
Eric Topol, MD is the executive vice president of Scripps Research Institute.
He believes that data gives us not only tools but also information that we have never before been able to access.
Topol has compared data’s ability to map the human body, and conditions to how Google AI maps offer satellite, traffic and street views of a location.
Topol explains that “We can quantify the environment, which we could never do before – now it’s obtainable information.”
This allows medicine and treatment to become more sophisticated and tailored to the individual.
By providing effective treatments, hospital stays and medical bills are cut. This makes the process more efficient.
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine – Top 10 Applications
Monitoring Medication Usage
Express Scripts deals with millions of prescriptions every year, working alongside retail pharmacies as well as operating a home delivery service.
The company is processing big data through high powered analytic applications.
The aim is to efficiently analyse a patient.
This means that the company will be able to alert health care workers to serious side effects before the patient has even been prescribed medicine.
The system can also identify patients who aren’t taking their medication.
This application has a number of potential benefits.
For example, the systems may be able to identify a patient at risk of becoming addicted to a certain medication.

By identifying this potential beforehand a different treatment plant can be selected.
Alternatively, the system will be able to predict the potential for a patient to fail to follow their post-hospitalisation medication regime.
This often leads to re-admittance.
However, if the patient is identified as being at risk, healthcare providers can provide a better level of support.
This can mean that re-admittance is avoided.
Tom Henry is the Vice President of Knowledge Solutions for Express Scripts.
He is leading the team working on these applications of big data.
Henry sees these predictive models as a means of avoiding “unnecessary treatment costs and improve patient outcomes.”
Henry believes that “Big data is good to have, but it’s meaningless if you can’t put it into action.
That’s what we do. By being proactive, we’re driving better decisions and healthier outcomes.”
Big Data Drives Self Driving Vehicles
Many automotive companies, such as Waymo, are working towards self-driving cars with Level 5 automation.
This means cars that are fully automated, and require no human involvement in order to navigate busy streets or highways.
To successfully achieve this goal big data analysis will need to be effectively harnessed.
Other automotive manufacturers are already collecting data from vehicles in a quest to improve the next generation of vehicles.

For example, Ford vehicles are fitted with sensors and software that collect data related to, amongst other things, fuel consumption.
This information can then be used to improve fuel efficiency.
Meanwhile, Aston Martin is collecting data concerning drivers habits with the aim of optimising engine performance.
Another example sees Tesla harvesting data via sensors to improve warning systems and collision detection.
These optional packages can be updated, meaning that Tesla vehicles are regularly improved.
All of this data can only be usefully gathered and analysed thanks to big data.
Helping Vehicles to see the World
BMW is working with location data service provider HERE to harvest big data from cars.
The company is using this information to develop technologies to control and regulate vehicle applications.
This includes features such as wiper or headlight use, braking force and navigation.
These applications of big data are helping BMW push towards its goal of developing cars with level 5 or full automation by 2021.
If full automation is to be realised analytics, as well as AI and machine learning, will play a key role.

This will primarily be in helping the vehicle to see and react to the world around it in real-time.
From fuel efficiency to parking sensors big data is already helping to make driving safer.
As understanding and implementation improve, it will continue to be key in helping automotive manufacturers reach level 5 automation.
Until then, however, big data will continue to make driving, and our roads safer.
Big Data in Marketing Understanding and Targeting Customers
The most well known of big data’s many applications.
This sees businesses leveraging data to better understand customer behaviour and preferences.
By using information gathered from social medial, browser logs, sensors and text analytics companies can expand the traditional data set.
An expanded data set allows the user to get a clearer, more rounded picture of the customer.
This application of data analysis allows Target, the U.S. retailer to accurately predict when a customer is expecting a baby.
Similarly, Wal-Mart is using these applications to predict what products will see at certain times of the year.
Meanwhile, telecom companies are using similar analytic applications to predict customer churn.
This application allows the company to get a clear picture of the interests, preferences and habits of a customer.
One of the most useful applications of this information is to create targeted or personalised marketing campaigns.
This sees businesses targeting potential customers with products that they are potentially interested in.
Netflix uses analytics to power their targeted advertising.
This allows Netflix to suggest movies or programs for customers to watch next based on past choice and other pieces of information.
Applying big data in this way allows Netflix to offer a personalised service.
It also helps the streaming service identify movies that are too scary to watch.
Big Data can Make us Safer
With budgets and manpower increasingly restricted, law enforcement agencies are under pressure to deliver a high level of service with fewer resources.
Being able to access data, such as criminal records can be vital but also costly and time-consuming.
Big data, if properly applied, can help officers access all this information quickly and efficiently.
With this in mind, modern police forces are harnessing as many technological applications as possible.
These include drones, computer vision powered body-mounted cameras, GPS systems, and Optical Character Recognition systems.
The Irish police force, the Garda, is teaming up with Siren, in an attempt to harness big data effectively.

Siren develops big data solutions, Natural Language Processing (NLP), AI and smart technologies with investigative forces in mind.
Giovanni Tummarello is the chief product officer at Siren.
He explained that “In law enforcement today, there are many fragmented technology tools –and this is a problem. Investigators use record management systems but often use separate graphical tools to draw connections as part of the ‘link analysis’ phase [when trying to pin down suspects].
The prevalence of disjointed software in many departments does not positively enhance the investigative process. Rather than act as an informative discovery process, no new information comes to the surface that investigators didn’t know already.
Investigative Intelligence, via Siren, is the ability to fuse previously disconnected analytics capabilities so that the investigator can freely ask questions – maximizing each individual technique.”
The Garda have been using the Siren platform across the Republic of Ireland.
From 2019 the platform is also being used by 10 European law enforcement agencies.
This is part of the EU’s Intelligence Network and Secure Platform for Evidence Correlation and Transfer project.

Cyber Security Solutions
Correctly identifying data, such as malicious interactions, is key to handling it correctly.
Encrypted environments allow for more secure big data environments to be built and maintained.
Big data can also be leveraged to generate predictive patterns.
These can allow businesses and organisations to predict not only customer behaviour but also attacks on their systems.
Big data’s ability to simultaneously take useful information from different sources allows users to optimise gathered information in almost real-time.
This potential has allowed the creation of efficient cybersecurity systems such as SIEM and IDS.
Similarly, the Panda Adaptive Defence 360 system leverages big data and machine learning to classify all events that occur on a computer network.
This allows organisations to detect and block any potentially malicious process.
Applications such as the Panda Adaptive Defence 360 are key to preventing breaches and data leaks.
Similar applications are allowing credit card companies to detect and block fraudulent transactions.
On a larger scale, the U.S. The National Security Agency has admitted to using analytics to foil terrorist attacks.
5 AI Cybersecurity Tools You Need To Know
Cyber Experts Warns Not to Perceive AI as a ‘Silver Bullet’
Big Data is Driving Product Development and Innovation
A big benefit of big data is that it helps companies to easily innovate and refine their products.
It allows for a product, and all the information surrounding it, to be analysed effectively and usefully.
This allows products to be optimised and refined.
Put simply, it allows products to be designed that fit exactly with what a customer needs.
Similar applications allow companies to identify new product lines and opportunities.
Amazon Fresh and Whole Foods are one company using analytics in this way.
Amazon leverages data analytics, allowing them to understand how customers purchase groceries.
Similar applications allow them to see how suppliers interact with grocers and retailers.
This information, properly processed, allows Amazon Fresh and Whole Foods to optimise their businesses and products.
This application allows Amazon to optimise and expand its grocery business.
The online giant is even planning on opening bricks and mortar stores.
While these stores may look traditional, they will still be focused on harvesting data.

Customers will need to log in on an app every time they enter a store.
Their physical choices can then be matched with online purchases.
This allows the company to form a better picture of their customers.
This allows Amazon to better use customer retention methods such as dynamic pricing to attract and retain customers.
Consequently, Amazon’s business model is optimised.
Improving and Optimizing Smart Cities and Countries
Big data can also have big applications.
It is already helping to optimise cities and even countries.
In Seoul, big data and the Internet of Things is also helping to keep the city streets clean.
Guillaume Weill is project director of Intralink.
He explained that the company’s “focus is on four main products, which have now been installed in more than 150 locations in Seoul, from parks to department stores, leisure venues and tourist districts.”

Seoul and Intralink have worked together to instal solar-powered waste bins, which compact rubbish automatically.
These use sensors to monitor waste levels in the bin.
A big data platform gathers this information helping to divert manual collections only when bins need emptying.
This application has helped to save cost and make Seoul a cleaner city.
Optimising Traffic Management
Meanwhile, in San Francisco, the cities Municipal Transportation Agency is using big data analytics to help prioritize transportation methods that aren’t cars.
This is part of the cities aims to provide a sustainable transportation system.
This vision includes a secure network of cycle-friendly streets.
San Francisco’s transportation agency uses smart monitors in the form of automated counters to monitor bicycle data.

This is regularly analysed, providing information on cycle usage in the city.
This application of big data analysis allows the city to see which areas are cycle friendly, and also helps to identify areas where people are reluctant to get on their bike.
This information allows the city to focus on improvement strategies for the most deserving areas.
Help to Find a Parking Space
In Stratford, Ontario officials are using big data applications to help people quickly find a parking space.
To aid this goal the city has installed 78 Internet of Things data-driven sensors.
These sensors merge information with GPS and data.
This information is relayed to Amazon Web Services MQTT Broker which sends the information to the Information Builders WebFOCUS data analytics platform.
This information is regularly updated alerting users to vacant spaces.
By helping people park their cars quickly Stratford officials believe that visitors will spend more time, and money, in local businesses.

Customer Acquisition and Retention
Without customers, a business will fail. This is true of every business.
To ensure that your business is a success you need to have a solid customer base.
This means acquiring and retaining customers.
For a business to retain customers they need to be able to move and grow with their customers, offering what their clientele wants, when they want it.
Big data allows a business to monitor customer patterns and trends.
The more information that a business holds on a customer the more trends or patterns it can identify.
Thanks to modern, digital technologies this process is easier than it has ever been, meaning that a business can easily monitor the behaviour of a customer.
By understanding a customer, or having an insight, the business can offer discounts or incentives based on past purchases.
Businesses can also identify customers that haven’t engaged with the brand for a while and attempt to reconnect with them.
Coca-Cola is Using Big Data to Adapt to Customer Needs
Coca-Cola is a global brand with a large market share. However, it doesn’t take its customer base for granted.
Coca-Cola uses big data to drive customer acquisition and retention.
One such example was seen in 2015. During that year Coca-Cola used a digital-led loyalty program to strengthen the company’s data strategy.
Coca-Cola has admitted that data is playing a key role in this process.
The Director of Data Strategy and Precision Marketing at Coca-Cola is Justin De Graaf.

In an interview, he revealed that “Data plays an increasingly important role in marketing and product development. Consumers do a great job of sharing their opinions with us – either by phone, email or social networks – that allow us to hear their voice and adjust our approach.”
De Greaafs comments reveal how aware the company is of the importance of listening to customers and adapting to their needs.
De Graaf added that “we’re working hard to use data to bring branded content that aligns with people’s passions.”
In 2017, the company revealed that their new drink Cherry Sprite was inspired and developed by information harvested via self-service drinks fountains.
These allow the consumer to mix their own drinks. By monitoring customer choices, this allowed Coca-Cola to identify the most popular flavour combination.
This was turned into Cherry Sprite.
Big Data in Supply Chain Management
Big data can help to improve the accuracy of supply chain networks.
It can also be used to provide clarity and insights into the management and operational process of the supply chain.
Most modern supply chain systems utilise big data.
This allows them to cope with complicated supply networks.
Adapted supply chains can also accurately adapt to knowledge sharing and collaboration.
By utilising data, supply chains are able to achieve a level of contextual intelligence.
One company that is making the most of data in the supply chain is PepsiCo.
A global snack food and drink company PepsiCo needs the supply chain to function at its most optimum level in order to be efficient.
This means ensuring that retailers always have the correct level and brands of their products in stock.
Data applications allow clients of PepsiCo to provide accurate reports on warehouse inventory and sale or demand levels of various products.
This information allows PepsiCo to meet the current demands of retailers.
It also allows them to predict future product demand levels and shipment needs.
This application allows PepsiCo to operate a smooth and efficient supply chain.

Big Data Will Only Grow in Importance
Big data analytics is a growing area of interest for many businesses and organisations.
Properly applied big data analytics can help a business to achieve an edge over rivals.
It can also help businesses to optimise processes and products, cut costs and retain a healthy customer base.
As technology continues to advance, and more money and time is invested in the area it is only going to grow in importance and usage.



















